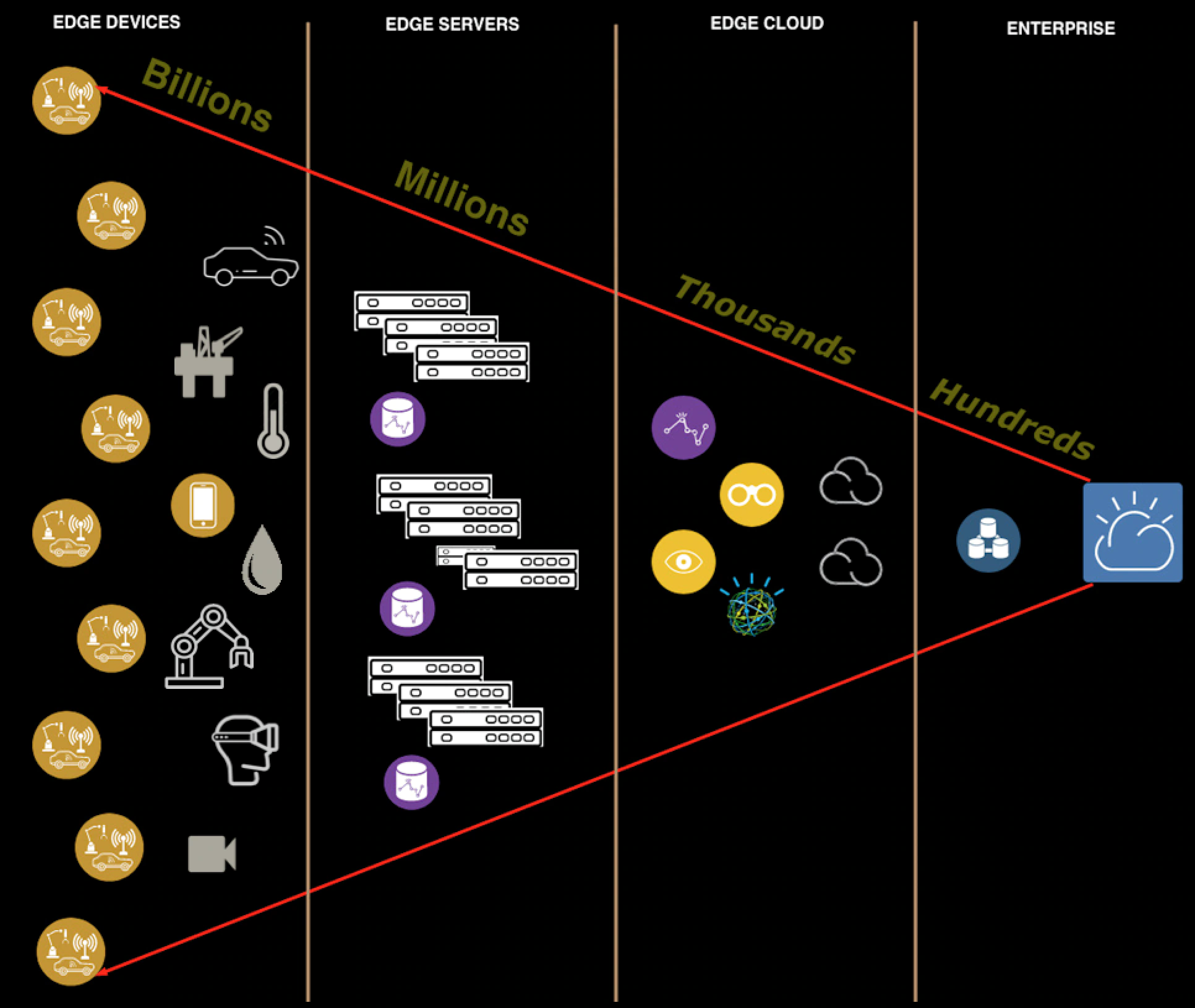
Why edge computing?
The unprecedented growth and expanding computing power of IoT devices has developed enormous volumes of data. These
data volumes will persist to grow as 5G networks expand the number of connected mobile devices. In the initial period of cloud,
the potential of cloud and AI was to automate and speed innovation by steering actionable insight from data. But the
unmatched scale and intricacy of data that’s created by connected devices has outperformed network and infrastructure
capabilities.
Forwarding all device-generated data to a consolidated data center or to the cloud triggers bandwidth and latency issues. Edge
computing proposes a more effective option; data is processed and analyzed closer to the point where it's produced. Because
data does not cross over a network to a cloud or data center to be processed, latency is drastically reduced. Edge computing and
mobile edge computing on 5G networks facilitates faster and more wide-ranging data analysis, establishing the opportunity for
deeper insights, swifter response times and enhanced customer experiences.
Edge computing assists you to unlock the potential of the vast untapped data that is created by connected devices. You can
uncover new business opportunities, increase operational efficiency, and provide swifter, more reliable and consistent
experiences for your customers. The best edge computing models can help you accelerate performance by analyzing data
locally. A well-thought approach to edge computing can keep workloads up to date, maintain privacy, and will adhere to data
residency laws and regulations.
An effective edge computing model should address network security risks, management complexities, and the limitations of
latency and bandwidth. A viable model should help you:
- Manage your workloads across all clouds and on any number of devices
- Deploy applications to all edge locations reliably and seamlessly
- Maintain openness and flexibility to adopt to evolving needs
- Operate more securely and with confidence
Gartner estimates that by 2025, 75% of data will be processed outside the traditional data center or cloud.